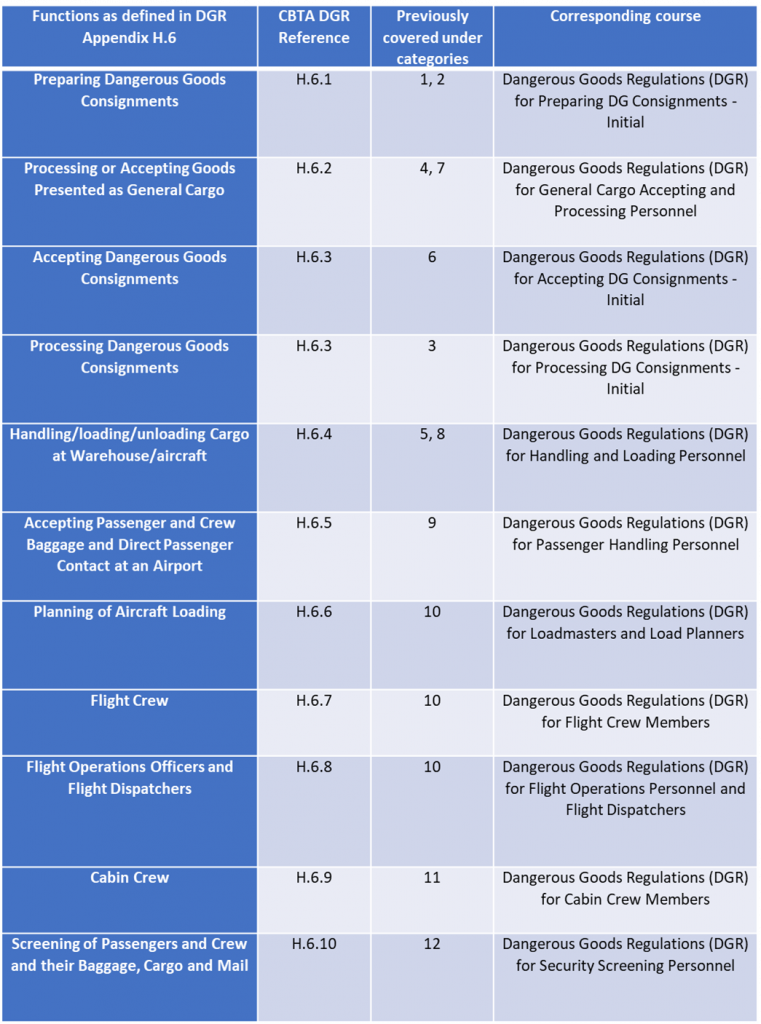
As of January 01, 2023, Dangerous Goods Rules (DGR) trainings have entered into a new training approach as Competency Based Training Assessment (CBTA).
For this reason, the categories in the current book of IATA DGR version 63 will be removed next year. For your convenience and to compare the traditional categories with the corresponding new courses, please review the table below.
Competency Based Training and Assessment Components
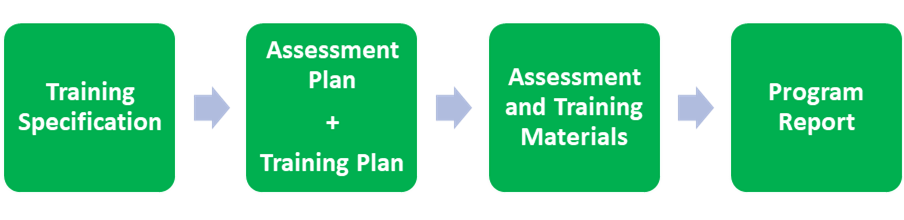
Therefore, the following components are essential for forming a competent workforce for the safe and efficient transport of dangerous goods by air:
- * A training specification that describes the purpose of training, the task list and the requirements that must be fulfilled when designing the training;
- * An assessment plan providing the process and tools for gathering valid and reliable evidence at different stages during training;
- * A training plan describing the training required to achieve the competencies;
- * Training and assessment materials, and any other organisational resources need to implement the training and assessment plans; and
- * A program evaluation report.
A competency is a dimension of human performance that is used to reliably predict successful performance on the job. It is manifested and observed through behaviours that mobilise the relevant knowledge, skills and attitudes to carry out activities and tasks under specified conditions to achieve a particular level of proficiency.
Competency Factors
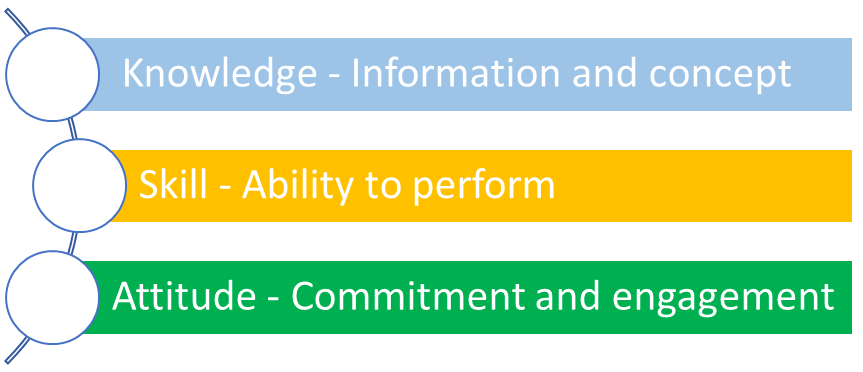
Performing a dangerous goods task may require different levels of knowledge, skills and attitude, depending on the complexity of the specific task and the operational environment. A level of proficiency should be developed to determine how critical the employee's knowledge, skills and attitude are for the successful completion of a task. Therefore, to determine the relevant level of proficiency of an employee's competency factors, the employer should consider the complexity of tasks and context, the range of work (routine, predictability, and dependencies) and the level of autonomy of the employee in performing the tasks.
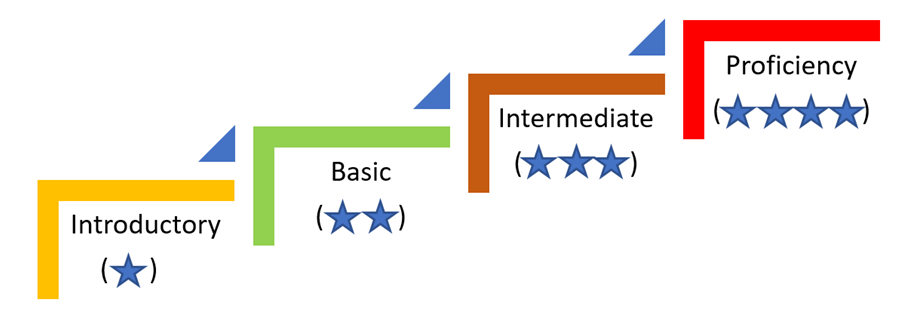
Proficiency can be divided into four levels, introductory, basic, intermediate and advance, and applied to individual tasks involved in the function(s) that an employee is assigned to.
Level of Proficiency
Competency Based Training and Assessment Workflows

Establishing competency-based training and assessment programs can involve five phases, analyse, design, develop, implement and evaluate. Here is a brief summary of each phase:
- Phase 1 - Analyse training needs: The first phase in the development and implementation of a competency-based training and assessment program is to analyse the training needs. Analysing the training needs is very important because the needs identified will form the basis of the type(s) of training and assessment methodologies to be required. Training needs are specific to the employer's environment and requirements, largely dependent on the internal process flow.
- Phase 2 -Design competency-based training and assessment (CBTA): Analysis of the training needs will form the foundation of the competency-based training and assessment program, and this phase will develop the backbone of the program. This phase includes designing two major components based on the training specification produced in the previous phase:
- an assessment plan that will be used to assess the competence of trainees;
- a training plan that will enable the development and delivery of the training course.
- Phase 3 -Develop the training and assessment materials: In this phase of developing and implementing a competency-based training and assessment program, the training designer will have to develop the training and assessment materials based on the training and assessment plans derived from Phase 2. Typical training and assessment materials include training notes, student handbook, case studies, presentations, video clips, examinations, practical exercises and on-the-job-observations.
- Phase 4 -Train in accordance with the training and assessment plans: When the training and assessment materials are well prepared, the training designers should determine the facilities and equipment, and training and assessment personnel required to conduct the training as planned. For the core dangerous goods training course(s), the course instructor will be the training and assessment personnel.
- Phase 5 -Evaluate the training and assessment program: HEM is responsible for ensuring the effectiveness of the training program. At the end of a period of training, feedback from the trainees, and training and assessment personnel should be gathered to deter-mine the effectiveness of the training and assessment program in supporting the progression of learning towards competence in the workplace. Evaluation of the training should be based on valid and reliable evidence such as course results, trainee feedback, reports from other training and assessment personnel, audit reports, and occurrence reports. This evaluation may lead to changes or improvements being made to the competency-based training and assessment design. Either the employer or their appointed assessor is responsible for evaluating the effectiveness of the training program. If this responsibility is outsourced to an appointed assessor, this person should be made familiar to the company's process in developing the whole program from the very first phase.